|
|
|||||||||||||
 |
|||||||||||||
|
I- SSC Identification and General Inventory: A preliminary activity based on the associative groups established in order to identify the integral amount of passive and active SSC that are accomplishing or not and that are sustaining or not an associated function, that have a long or specified life duration , with or without moving parts, with or without changing their properties or configuration. An associative group contains SSC arranged in a rational manner according to their similarities (design, fabrication materials, ageing assessment methodologies, working environments). Major Associative Groups:
Minor Associative Groups:
Associated Function: a set of intrinsic characteristics and/or operational features which must be satisfied in any operating or accident conditions during plant design life, including the extended period, such that plant operability status and its essential safety functions to be accomplished. The associated functions are made-up from the following groups of primary functions: a - Process Function = a function assigned to a SSC in order to sustain actively or passively nuclear, thermal,mechanical, hydraulic, thermodynamic, chemical and electrical processes required by the specified operational status and its performance and operability requirements. b - Nuclear Safety Function = a function assigned to a SSC in order to sustain actively or passively its preventive and/or protective characteristics and whose effectiveness is required by the essential nuclear safety functions accomplishment, during operating regimes and postulated accident conditions. c - Passive Function = a function assigned to a passive SSC which act in support of safety and/or process functions. II - SSC Scoping: The identification process of those plant parts (SSC) which are the objective of nuclear facility licensing renewal and that are submitted to selection process. A structure, system or component is classified if at least one scoping criterion is fulfilled. The following are the scoping criteria established for CANDU-6 plant:
III - SSC Screening: The identification process of those plant parts (SSC) which are the objective of licensing renewal and that shall be evaluated in order to assess their ageing degradation or to identify the exceptions, if any. A structure, system or component is selected if at least one of the following criteria is met: 1 - SSC is Safety Related and it must be remain operational during and after a design basis event in order to provide that essential safety functions are met; 2 - SSC is Not Safety Related but its failure could impair at least one essential safety function completion (missiles production, flooding, large weights or fuel handling errors, HE systems impairment); 3 - SSC is SR or NSR but which are credited in safety analyses or plant assessments complying with specific associated function, during specified event classes (Fires, L-LOCA, Thermal shock,ATWS, LOCLIV).
IV - Selected CANDU-6 SSC categories: 1 - Limiting Critical SSC = those SSC for which:  , or a Life Cycle Management plan. , or a Life Cycle Management plan.
2 - Critical SSC = those SSC for which: 
3 - Important SSC = those SSC for which:
4 - Not important SSC = those SSC which:  sessment/surveillance programs prescriptions for components. sessment/surveillance programs prescriptions for components.
|
|||
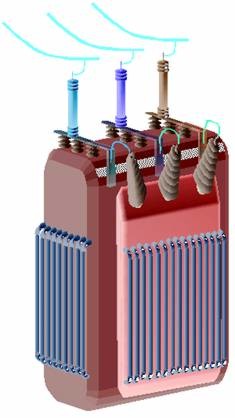 trumentation & Control Systems
trumentation & Control Systems